
Blood Can Be Very Bad! How to Read an Emergent Head CT — Downeast Emergency Medicine
Cisternostomy is a surgical technique thought of and developed as an option for severe brain trauma treatment. It demands a particular knowledge and skill to microsurgically approach basal cisterns and effectively manipulate their contents. To perform this procedure safely, the anatomy and pathophysiology must be clearly understood. Methods:

suprasellar cistern anatomy
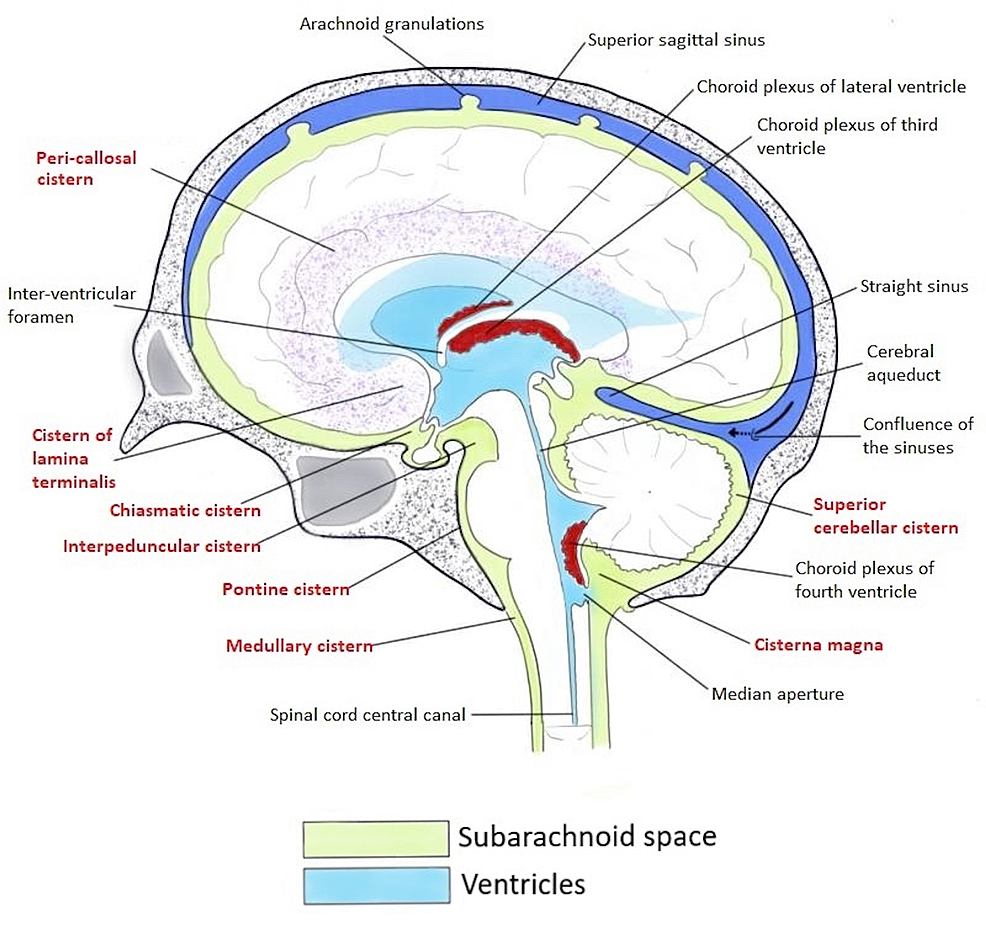
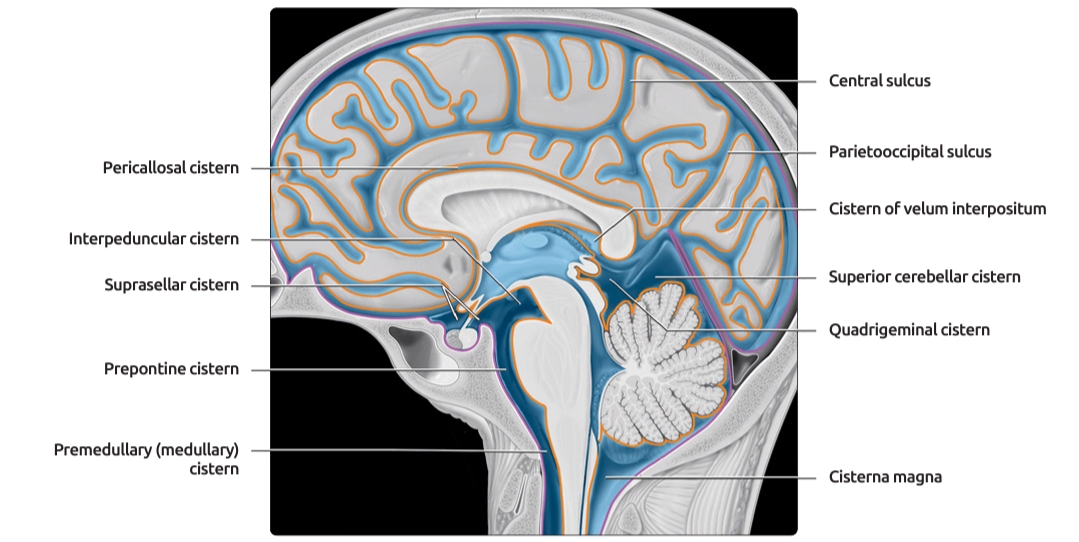
Ambient cistern (Figure 6): Located in the lateral aspect of the brain stem. This cistern has a particular surgical importance as it has both supratentorial and infratentorial extensions. Divided by the superior cerebellar membrane, the superior compartment or posterior cerebral ambient cistern houses the posterior cerebral artery, medial and.

MRI Brain ambiens cistern anatomy Radiology Anatomy Images Mri brain, Mri, Brain anatomy
The anterior circulation of the brain is related to the subarachnoid cisterns of the supratentorial region and the cisternal approach to the supratentorial lesions consists of a compartmental opening of one or more of these cisterns (88, 97, 98, 100, 105-107). Any lesion may grow epiarachnoidally or also within one or more cisterns but, in both.
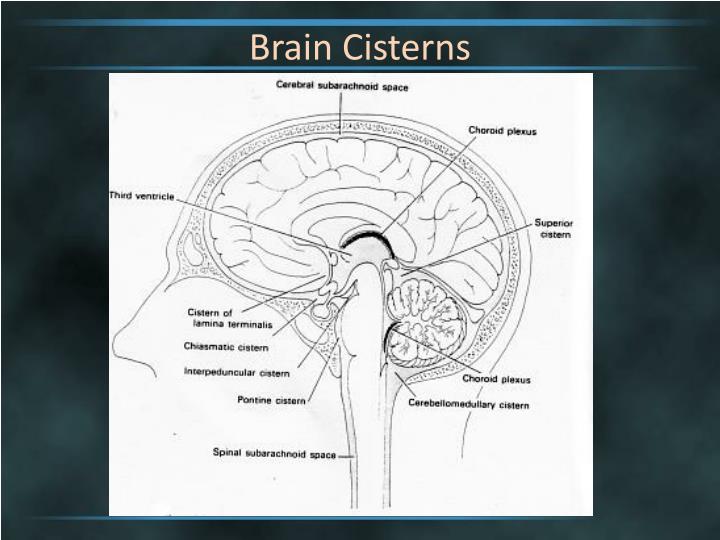
PPT Brain Cisterns PowerPoint Presentation ID2263744
The ambient cistern is a thin, sheet-like extension of the quadrigeminal cistern that extends laterally around the midbrain and posterior to the thalami. It acts as the connection between the quadrigeminal cistern and the interpeduncular cistern.

PPT Brain Cisterns PowerPoint Presentation ID2263744
The interpeduncular cistern is located at the base of the brain at the junction where the arachnoid mater stretches between the two temporal lobes, occupying the interpeduncular fossa. Located within this cistern is the optic chiasm as well as some important neurovascular structures which include:.

2 Ventricles and Cisterns Radiology Key
A cisternogram scan is a diagnostic procedure that evaluates how cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows around your brain and spinal cord. This protective fluid: Delivers nutrients to your brain and spine. Helps your central nervous system (CNS) work. Removes toxins from tissues in your CNS. Acts like a cushion to protect your brain from concussion.

6 Basal Cisterns Anatomy Neupsy Key
The concept of intracranial surgery in terms of moving from one cistern to another is presented here with particular emphasis on the cisterns in surgical approaches to intracranial vessels and nerves for the treatment of aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and for surgery of basal tumors. MeSH terms Brain / blood supply
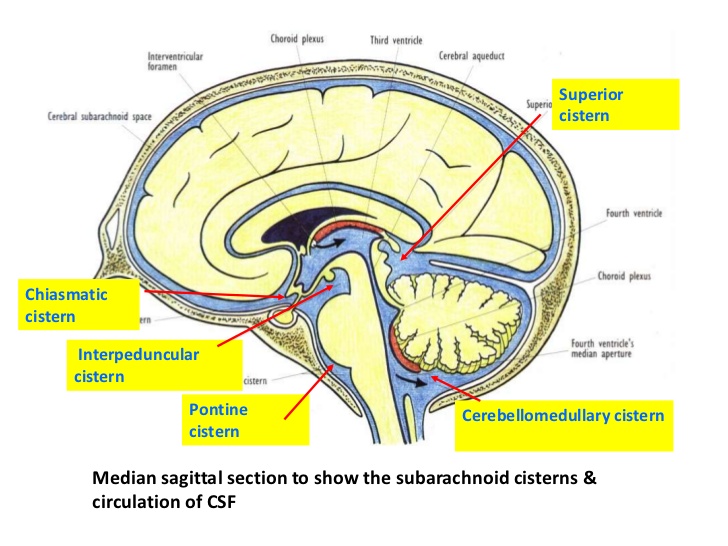
Basal CSF cisternsInterpeduncular cistern RANZCRPart1 Wiki FANDOM powered by Wikia
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. [1] The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). [1] Structure

Subarachnoid Cisterns Anatomy YouTube
CT Brain Anatomy CSF spaces Key points The CSF spaces comprise the sulci, fissures, basal cisterns and ventricles An appreciation of the normal appearances of the CSF spaces is required to allow assessment of brain volume The brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) within the sulci, fissures and basal cisterns.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/452/744UeLdRamXVwT6d4CThA_subarachnoid-cisterns-of-the-brain_english__1_.jpg)
Subarachnoid cisterns Anatomy and clinical points Kenhub
The epidural space in the skull is a potential space, while it is actually present in the spinal cord. The subarachnoid space consists of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), major blood vessels, and cisterns. The cisterns are enlarged pockets of CSF created due to the separation of the arachnoid mater from the pia mater based on the anatomy of the.
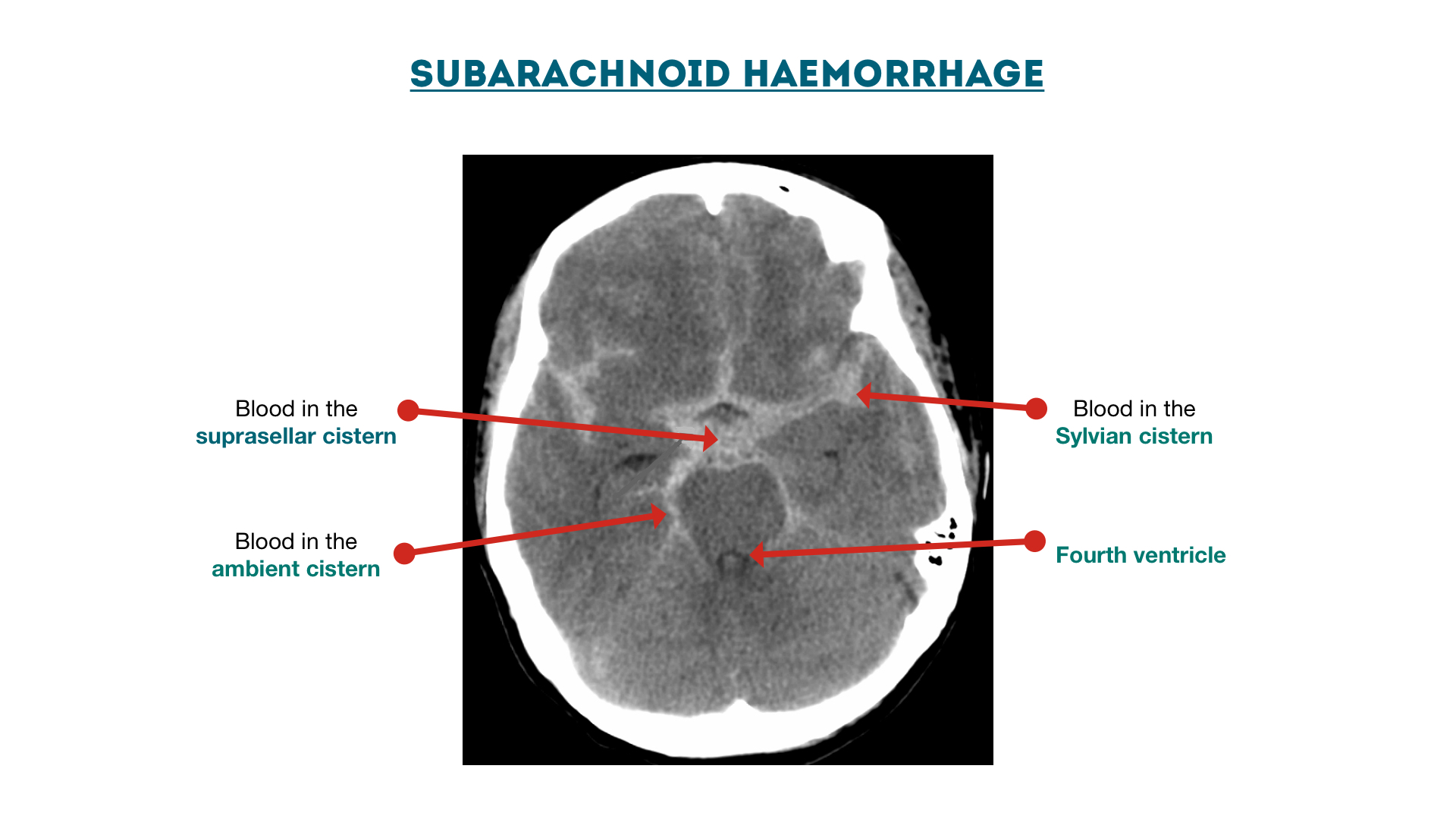
Subarachnoid haemorrhage cisterns Geeky Medics
Normal Anatomy The ventricular system is located deep within the brain and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The normal appearance of CSF on magnetic resonance images is that of water. This axial MR image shows the choroid plexus within the ventricles, where CSF is produced.
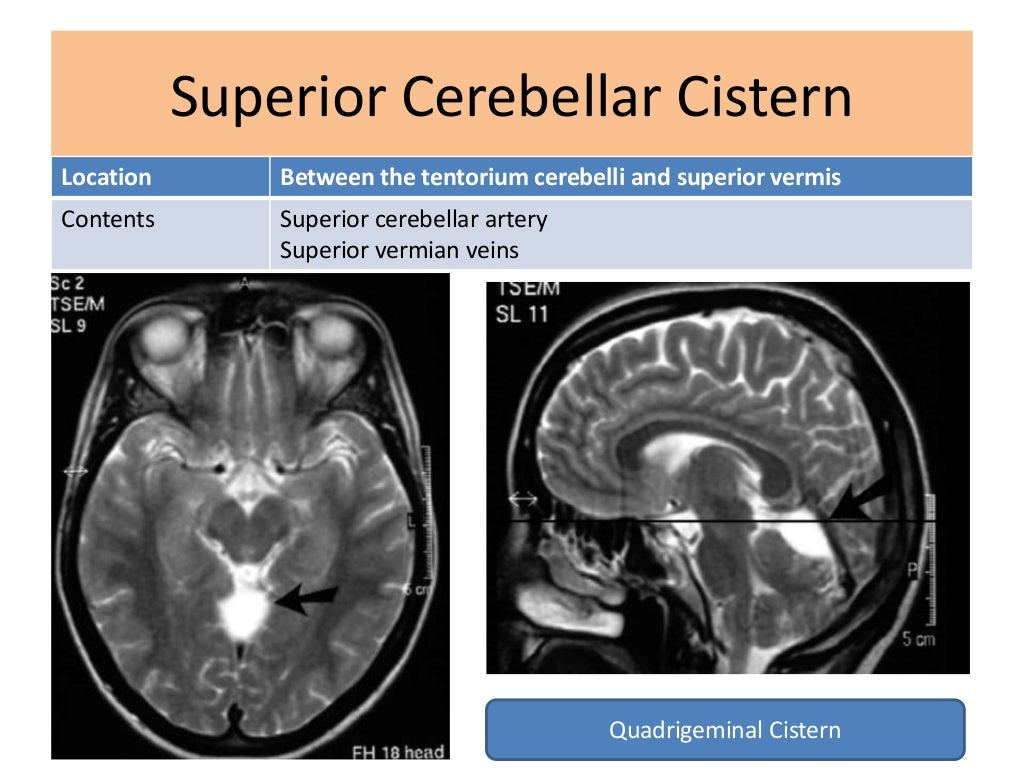
Cisterns of brain and its contents along with its classification and
Definition and location of the falx cerebri. The brain is bathed in fluid during life. The name of this substance is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It provides the brain with nutrients, allows for solute exchange, and provides basic mechanical and functional support to the organ.
Cureus Delineation of Subarachnoid Cisterns Using CT Cisternography, CT Brain Positive and
P, Posterior. Brain MRI: coronal T1-weighted cut. 1, Interpeduncular cistern. 2, Hippocampus. 3, Third ventricle. 4, Lateral ventricle. Ambient cistern Brain MRI: sagittal T1-weighted cut. 1, Ambient cistern. 2, Splenium, corpus callosum. 3, Cerebellum. 4, Pons.

PPT Brain Cisterns PowerPoint Presentation ID2263744
The interpeduncular cistern is an unpaired CSF-filled subarachnoid cistern located between the cerebral peduncles. It is partially bounded by the leaves of the Liliequist membrane, one of the arachnoid membranes , which separate it from its direct cranial and caudal relations 1.

Normal sagittal midline MRI showing the CSF cisterns. A. Cistern of the laminae terminalis. B
The subarachnoid space is described as a cistern at points where spaces exist between it and the underlying pia mater. At different points around the brain, the cisterns are described with respect to adjacent anatomical landmarks. Notable cisterns include the: suprasellar or chiasmatic cistern; interpeduncular cistern; prepontine cistern
ventricular system overview Brain Imaging
0:00 / 15:04 Ventricles and Cisterns of the Brain | Radiology anatomy part 1 prep | MRI brain Radiology Tutorials 37.3K subscribers Subscribe 715 20K views 1 year ago Anatomy Tutorials High.